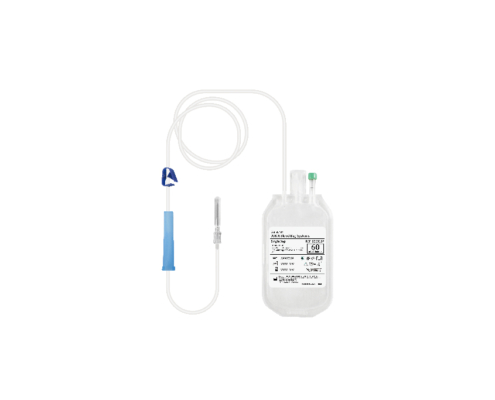
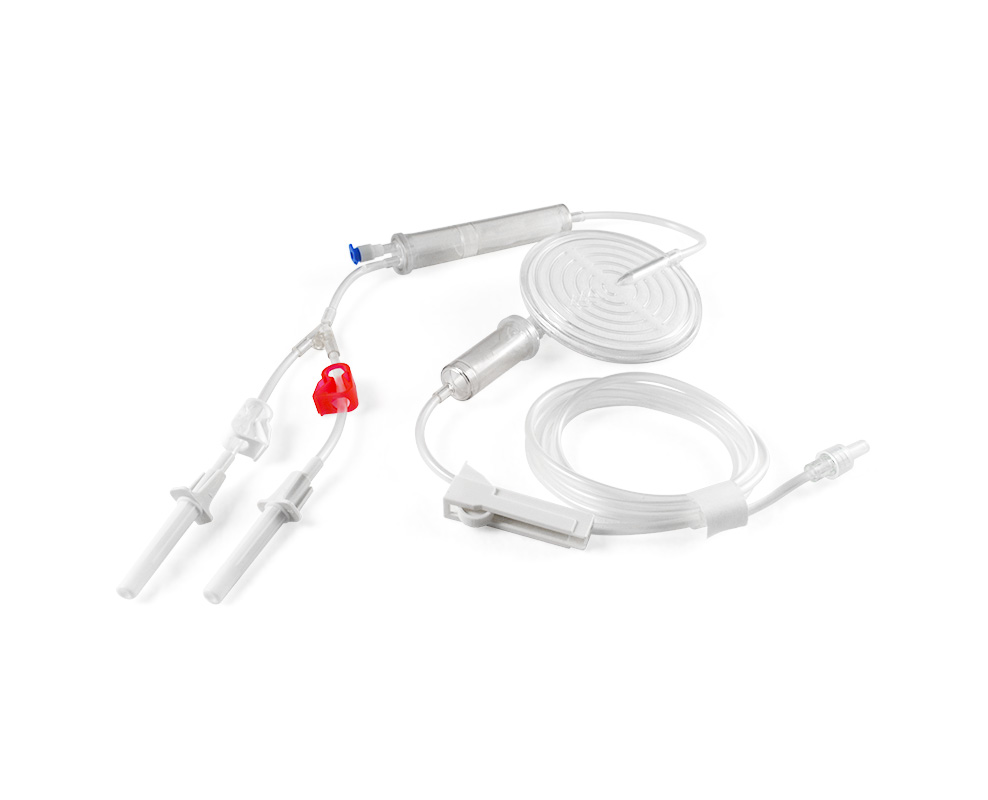
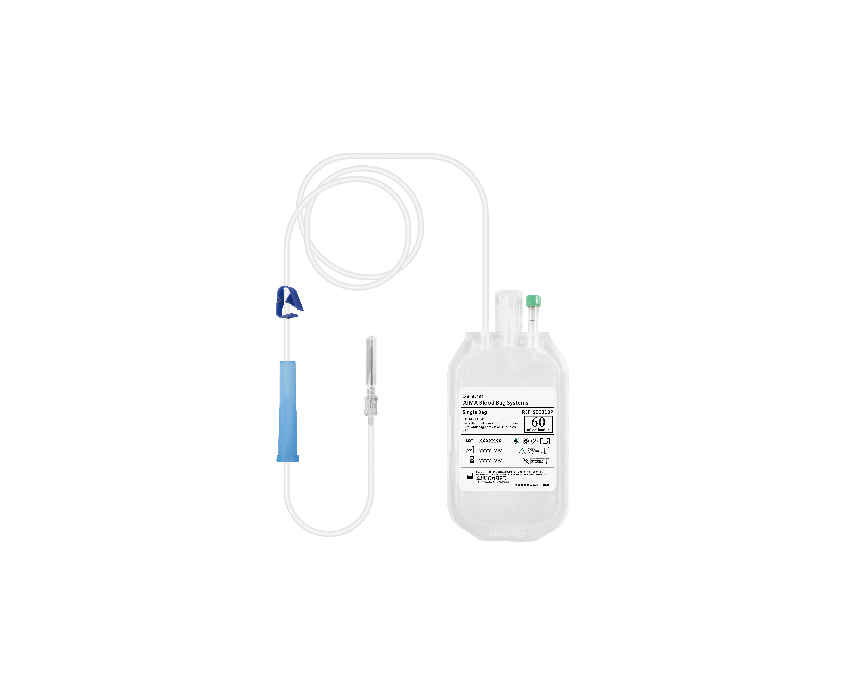
What is blood components ?
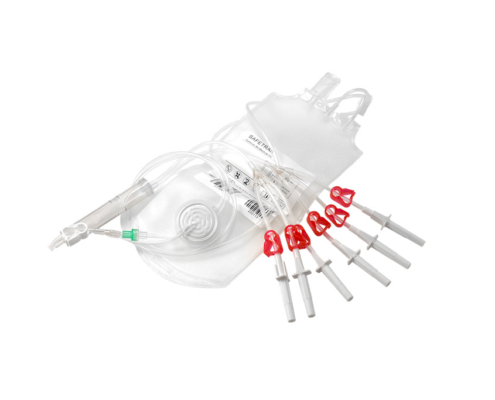
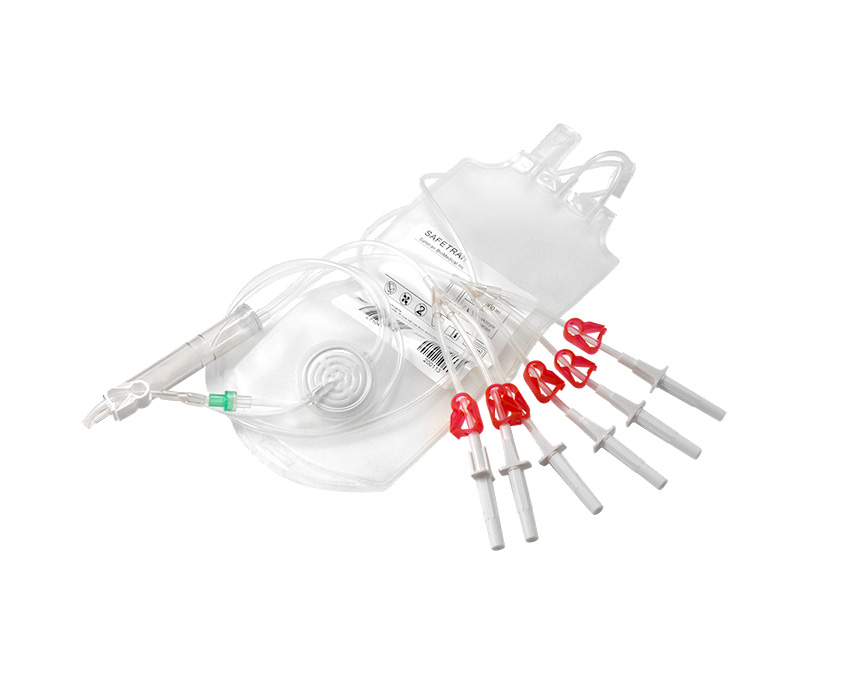
The composition of blood consists of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. During the process of blood transfusion, clinical practice seldom transfuse whole blood; instead, blood components are administered based on the specific needs of the patients, to increase blood product utilization.
Here are some common blood products:WB(Whole Blood),PRBC(Packed Red Blood Cell),PC(Platelet Concentrates),and FFP(Fresh Frozen Plasma).